Screening of patients receiving selegiline from methamphetamine abusers using the urinary amphetamine/methamphetamine ratio
Abstract
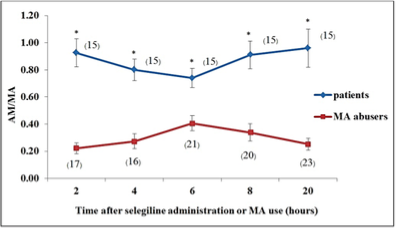
Methamphetamine (MA), the major metabolite of selegiline excreted in urine, can cause false positive interpretation of patient receiving selegiline as a MA user based on the routine non-chiral separation method. This study aims to compare the ratio of amphetamine (AM) to MA concentrations in urine of patients receiving selegiline and MA abusers. Urines were collected from fifteen patients at 2, 4, 6, 8 and 20 hours after selegiline administration. Urines from 97 MA abusers were collected at 2, 4, 6, 8 or 20 hours after the last exposure. AM and MA concentrations were determined by solid phase micro-extraction gas chromatography/ mass spectrometry. The results showed that urinary AM/MA ratios in the patients were significantly higher than those of the MA abusers at every time point. The lowest AM/MA ratio in the patients was 0.74 ± 0.07 and the highest AM/MA ratio in the MA abusers was 0.41 ± 0.05 at 6 hours. Thus, urinary AM/MA ratio could be used for preliminary differentiation of patients receiving selegiline from MA abusers with an accuracy of 84.88% when using a ratio of 0.40 as the cutoff value.
Full Text:
161-170:PDFRefbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.

